Campaign 2020
Every Drop Counts
Climate Resilience starts with Water
We experience severe impacts of climate change through water, especially in water availability and quality. In many regions, climate change intensifies water scarcity, heavy rainfalls and flood events. Effects are already visible across the economy. Therefore, German development cooperation supports actions to strengthen climate resilience through policies, technical and nature-based solutions.
Diagramm 1
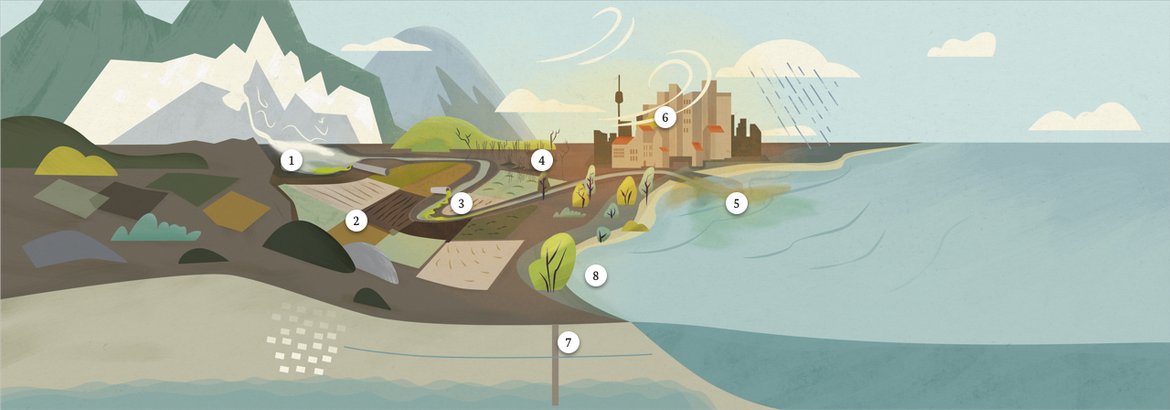
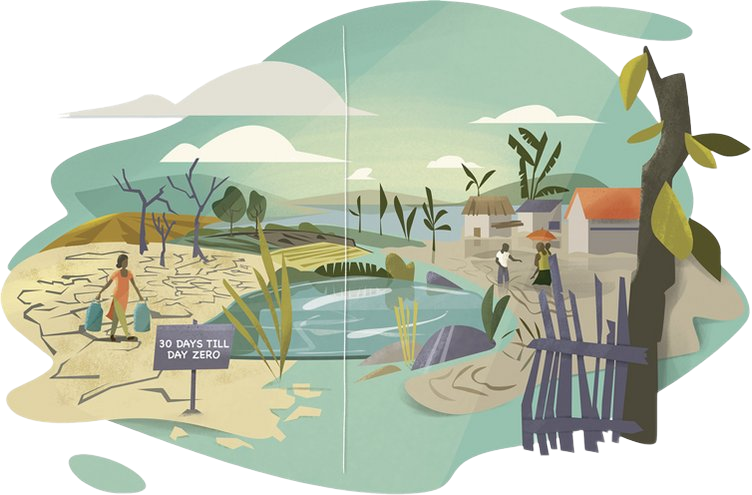
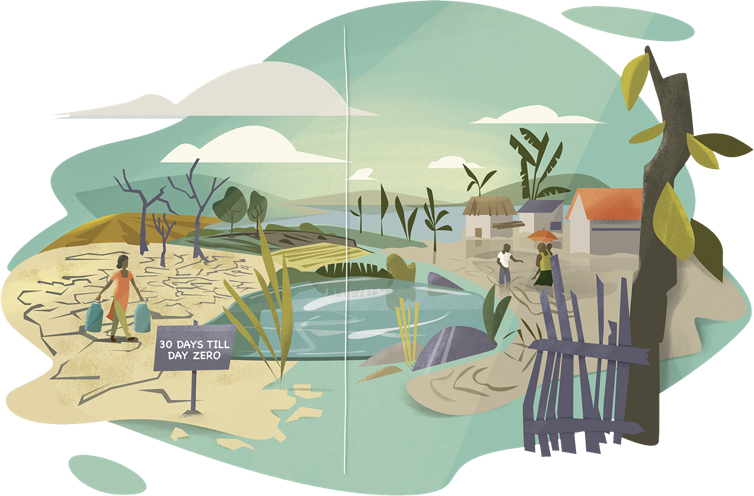
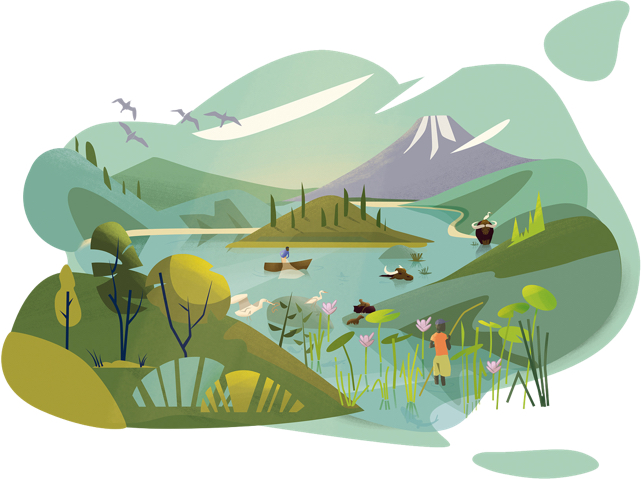
This landscape represents the impacts of climate change until the year 2050 without ambitious climate action. Relevant megatrends of increasing urbanization and intensified agriculture characterize the scenery. Standard measures are not sufficient to compensate for uncertainty and intensity of precipitation. Glaciers have melted almost completely, groundwater storages are depleting, the sea level keeps rising. Water scarcity and flood events are occurring frequently on a global scale, the loss of ecosystems and species is accelerating.
- Rapidly melting glaciers reduce natural water storage
- Intensive farming reduces diversity and increases inputs of fertilisers and pesticides
- Harmful inputs into watercourses impair usability and biodiversity
- Dry wetlands are ruining the atmosphere
- Discharges of wastewater and waste into the oceans must be prevented
- Climatic conditions in cities quickly become hostile
- Groundwater storage reduced
- Without protective coastal ecosystems, floods and sea-level rise will become more threatening
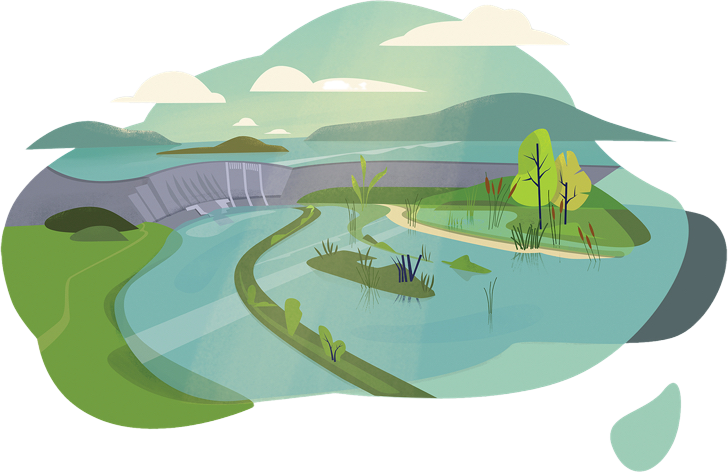
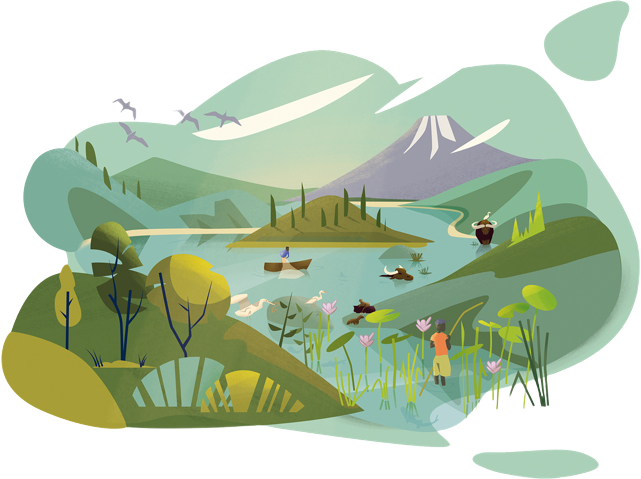
Diagramm 2
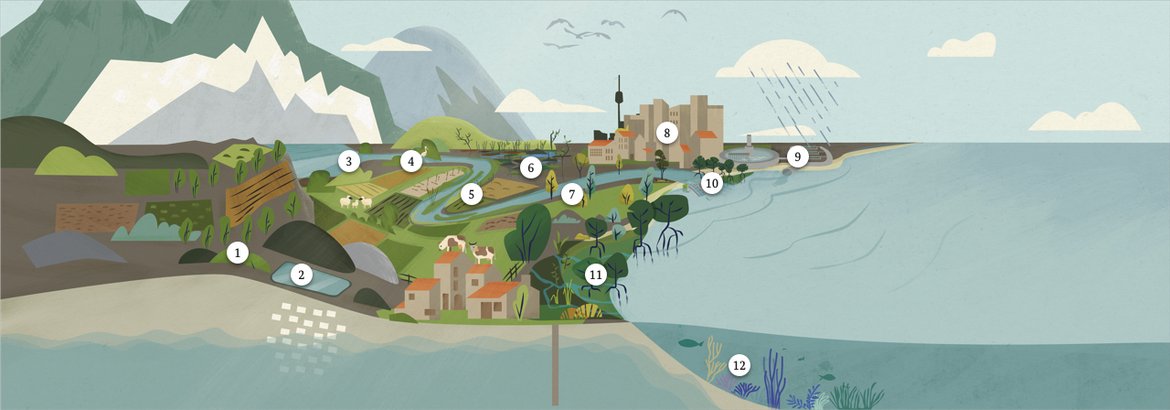
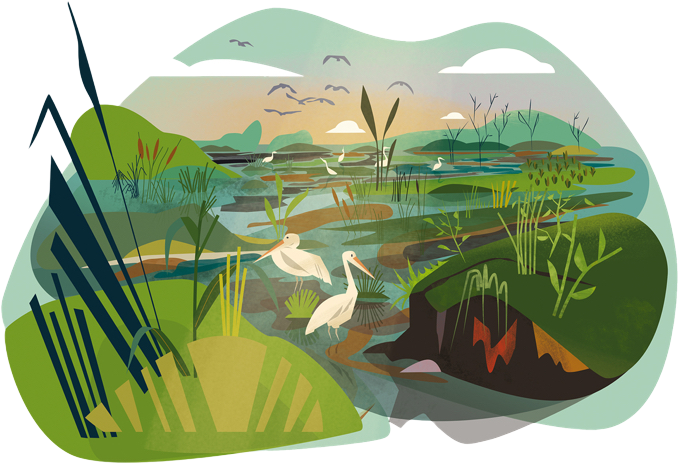
This landscape represents the impacts of climate change until the year 2050 with total political and economic commitment to climate action and a 1.5°C goal.
- Agroforestry to prevent erosion
- Flexible water storage
- Lakes as water reservoirs and places of diversity
- Running waters as dynamic interface
- Ecosystem-based approaches
- Wetlands to reduce emissions
- River commissions for cooperation and conflict prevention
- Cities are innovation centers for integrated solutions
- Sustainable sanitation systems are resistant to greater fluctuations in precipitation and wastewater volumes
- Robust solutions include barriers to protect against storm surges or to regulate the flow
- Mangroves as a species-rich ecosystem are an ideal carbon store and grow with the rise in sea level to protect against flooding
- Healthy freshwater ecosystems prevent harmful inputs into threatened coral reefs as a hotspot of biological diversity
Campaign
Discover our contributions to the water climate theme year 2020
We are feeling the massive effects of climate change through water, especially in terms of water availability and quality. Find out more about German Development Cooperation measures to strengthen climate resilience in the water sector.








